Press ReleasesNippon Paper Industries Verifies suppressive effect of High-performance Tea 'Sunrouge' on Metabolic Syndrome Confirmed in Animal StudiesInhibitory effect of α-glucosidase activity in Sunrouge is 2.4 times higher than that in Yabukita Highest effect among the 51 major Japanese tea cultivars
Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd.
Nippon Paper Industries Co., Ltd. (President: Fumio Manoshiro) evaluated suppressive effect of 'Sunrouge' on metabolic syndrome through a collaborative study with Kyushu University (Prof. Hirofumi Tachibana) and found that Sunrouge has the highest inhibitory effect of α-glucosidase, a digestive enzyme that hydrolyses polysaccharides such as starch into glucose, among the 51 major Japanese tea cultivars including Yabukita. In addition, Nippon Paper Industries verified that in a study on mice, Sunrouge has a suppressive effect on the elevation of the postprandial blood glucose level and on the elevation of HOMA-IR (a method for evaluating insulin resistance), which is an indicator of hyperglycemia. Nippon Paper Industries plans to present these results at the 2015 Annual Conference of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry on March 28 (Note 1.).
Metabolic syndrome is a multiplex risk factor in which two or more conditions such as hypertension, hyperglycemia, or dyslipidemia exist in addition to visceral fat accumulation and is known to cause lifestyle-related diseases such as myocardial infarction, stroke, and diabetes. Recently not only middle-aged or elderly adults but also children increasingly suffer from metabolic syndromes, which is a social issue from the point of view of public health.
On the other hand, it has increasingly been clarified that intake of a component of green tea is effective on anti-metabolic syndrome including improvement of lipid metabolism and prevention of obesity.
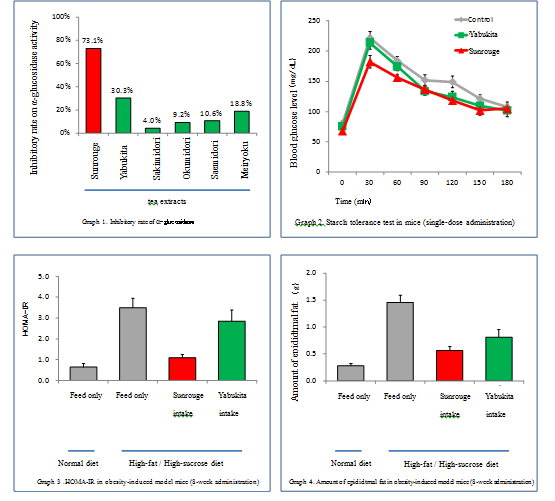
Nippon Paper Industries and Kyusyu University clarified that among the 51 major Japanese green tea cultivars, Sunrouge has the highest inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase by 2.4 and 18.4 times higher as compared with Yabukita and Sakimidori which has the lowest effect (Graph 1.), respectively.
In addition, in a study on mice, Sunrouge suppressed the elevation of the blood glucose level up to 18% at 30 minutes after a starch feeding compared to Yabukita (Graph 2.). Furthermore, Sunrouge was verified to suppress elevation of HOMA-IR (a method for evaluating insulin resistance), which is an indicator of hyperglycemia (Graph 3.) and suppress the accumulation of body fat (Graph 4.).
Sun Rouge is a new tea variety containing anthocyanin (a plant-based functional ingredient) and is developed using Nippon Paper Industries' original "In-container rooting technology[A1]" based on a photo-autotrophic culture system, jointly with the National Agriculture and Food Research Organization and the National Institute of Vegetable and Tea Science. Sunrouge has anti-fatigue and anti-stress effects by a synergy effect of catechin and anthocyanin, and it is expected to create a new demand as a high-performance tea that improves eyestrain.
While Sunrouge's function of improvement metabolic syndromes effectively has been confirmed in this study, Nippon Paper Industries will further verify the effect of Sunrouge on humans with Kyushu University. At the same time, the Agri-business of Nippon Paper Industries will work positively to develop the market that takes advantage of the function of Sunrouge.
Note 1:The 2015 Annual Conference of the Japan Society for Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Agrochemistry
Dates: March 26 (Thursday) to 29 (Sunday), 2015
Venues: Hotel Granvia Okayama and the University of Okayama, Tsushima Campus