Dissolving Pulp (Sulfite)Dissolving Pulp (Sulfite)
Features

Cellulose, which accounts for about half the content of wood, and hemicellulose components, have long been used as the raw materials of paper and pulp. Our dissolving pulp has been widely used particularly as the raw material of rayon and cellophane as it is produced by sulfite pulping, further enhancing cellulose purity.
Our pulp also has a high whiteness, since hemicellulose and lignin content is low, and not only is it used as an important raw material of CMC (Carboxymethyl cellulose) and other cellulose derivatives, as well as the base material of heat hardened resins (mainly urea and melamine resin molding material), but it is also ideal as a chemically transformed raw material, and it is also widely used as papermaking pulp (specialty paper).
- Inquiries
-
- Telephone
-
Chemical Sales Dept.Ⅱ
+81-3-6665-5960
Structure
Cellulose is the main element of wood and one of the most important materials on earth. Structures differ slightly between softwood and hardwood as the table below indicates. NPI manufactures high-alpha cellulose pulp by cooking the sulfites under high temperature and pressure.
| Elements | Softwood | Hardwood |
|---|---|---|
| Cellulose (%) | 49-58 | 50-62 |
| Hemicellulose (%) Hexosan (%) Pentosan (%) |
8-24 4-12 4-12 |
20-33 2-6 18-27 |
| Lignin (%) | 23-32 | 18-24 |
| Others (%) | 1-4 | 1-6 |
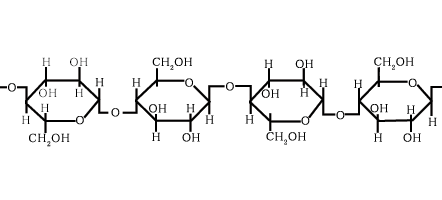
Chemical structure of cellulose
Cellulose is a high polymer compound made up of three elements, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is an environmentally friendly substance because it is a carbohydrate like starch or sugar.
-
[Molecular formula (C6H10O5)n]
The structure of cellulose is a long chain of units of glucose.
Comparison of fibers between softwood and hardwood
The following table shows a comparison of fibers between softwood and hardwood.
The fibers of softwood are generally longer and thicker than those of hardwood.
| Softwood | Hardwood | Comparison | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main elements |
Tracheids >approx. 90%, Parenchyma cells >approx. 10% |
Wood fiber: 60~80%, Parenchyma cells: 10 - 30%, Sap vessels approx.: 10% |
Hardwood contains more parenchyma cells. |
| Length(mm) | 1.5 - 5.5 | 0.5 - 2.3 | HW is less than 1/3 of SW. |
| Width(mm) | 0.039 - 0.043 | 0.021 - 0.024 | HW is less than 1/2 of SW. |
| Length/width | 88 - 103 | 52 - 63 | HW is 50-60% of SW. |
| Thickness of cell membrane(mm) | 0.001 - 0.003 | 0.003 - 0.006 | HW is approx. two times thicker than SW. |
- Inquiries
-
- Telephone
-
Chemical Sales Dept.Ⅱ
+81-3-6665-5960
Properties
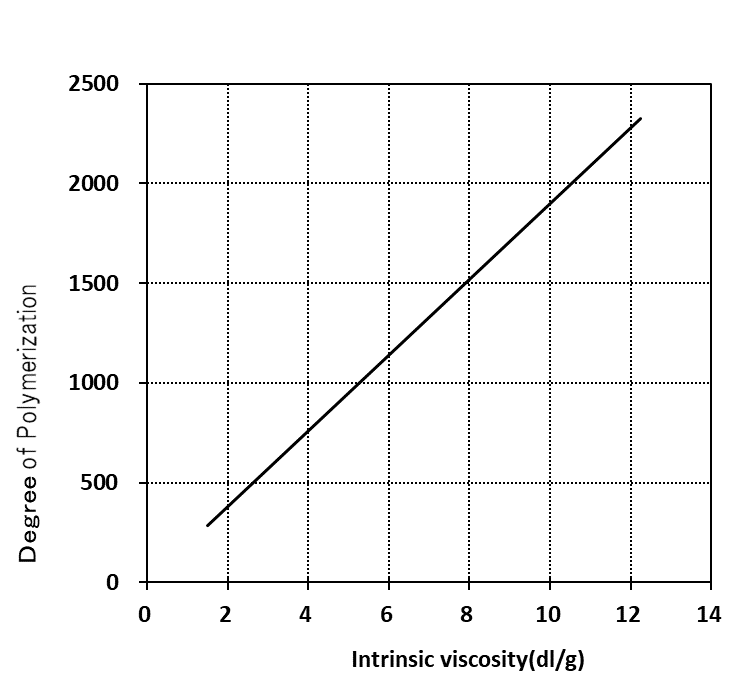
Degree of polymerization
Solvent
| Solubility | Oxidative decomposition | Stability | Color | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Copper ammonium hydroxide | good | yes | unstable | blue, clear |
| Copper ethylenediamine | good | yes | unstable | blue, clear |
Main uses of pulp
| Viscose rayon | Viscose rayon include not only regular rayon and high tenacity rayon but also polynosic rayon (for clothing). Each comes in the form of rayon staples or rayon filaments. The pulp of higher cellulose purity is used for high quality filaments and polynosic rayon rather than for staples. |
|---|---|
| Cellophane | While rayon is made by extruding viscose through spinnerets to form thin strands, cellophane is made by extruding viscose through a long narrow slit to solidify and reconvert the viscose into a film. |
| Acetate |
Acetate is a semi-synthetic fiber. It is created by chemical reacting pulp with acetic acid. Its distinctive characteristics include a silky touch and luster. In addition, its high color-forming ability allows acetate to be used on textile fabrics. |
| Plastic filler | Our pulp is used as a filler for plastic urea and melamine resin products, and the finished products are widely used in electrical machinery parts, tableware, toys and other products. |
| Cellulose derivative | As a raw material of cellulose derivatives, pulp is used in CMC (Carboxymethyl cellulose), MC (Methyl cellulose), HPC (Hydroxypropyl cellulose), HEC (Hydroxyethyl cellulose), etc. Powdered cellulose is pulp that has undergone acid hydrolysis, been mechanically disintegrated and made into a fine powder. |
| Specialty paper | Since our pulp is produced by sulfite pulping and is highly refined, it is a product of high whiteness with few impurities. With these features, our pulp is used widely in specialty paper-related products such as filter paper and vulcanized fiber. |
- Inquiries
-
- Telephone
-
Chemical Sales Dept.Ⅱ
+81-3-6665-5960
Grades
NPI provides various grades of pulp.
| α cellulose(%) | Intrinsic viscosity(dl/g) | Whiteness(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSPP-HR | ≧ 93 | 8.0 - 10.0 | ≧ 93 |
| NDPT | ≧ 90 | 4.5 - 6.0 | ≧ 92 |
| NBSP | ≧ 87 | 5.5 - 9.0 | ≧ 90 |
| LNDP | ≧ 89 | 4.5 - 6.0 | ≧ 92 |
| LDPT | ≧ 90 | 4.5 - 6.0 | ≧ 92 |
| NDPS | ≧ 90 | 10.0 - 12.0 | ≧ 90 |
※The above numbers are for reference only.
α cellulose: Degree of non-dissolution in 17.5% NaOH water solution.
Intrinsic viscosity: ISO 5351 reffered.
Whiteness: ISO 2470-1 referred.
Packaging
Sheet pulp:200kg/bale (10% moisture)
Size:600mm(L) × 800mm(W) × 460mm(H)
Packaging:Lashing wire 2×2, wrapped with paper or non-wrapped
Roll pulp (NSPP-HR):Approx. 300kg/roll (10% moisture)
Size:710mm(W) × 1000mm(D)
Packaging:non-wrapped, coreless
- Inquiries
-
- Telephone
-
Chemical Sales Dept.Ⅱ
+81-3-6665-5960
Uses
| Synthetic fiber | Cellophane | Cellulose derivative | Plastic filler | Specialty paper | Acetate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rayon Polynosic | Sticky tape film | CMC HEC, HPC | Plastic urea/melamine resin | Filter paper, Specialty paper | Cigarette filters | |
| NSPP-HR | ○ | ○ | ||||
| NDPT | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ | |
| NBSP | ○ | |||||
| LNDP | ○ | ○ | ||||
| LDPT | ○ | ○ | ○ | |||
| NDPS | ○ |
CMC: Carboxymethyl cellulose
HEC: Hydroxyethyl cellulose
HPC: Hydroxypropyl cellulose
- Inquiries
-
- Telephone
-
Chemical Sales Dept.Ⅱ
+81-3-6665-5960